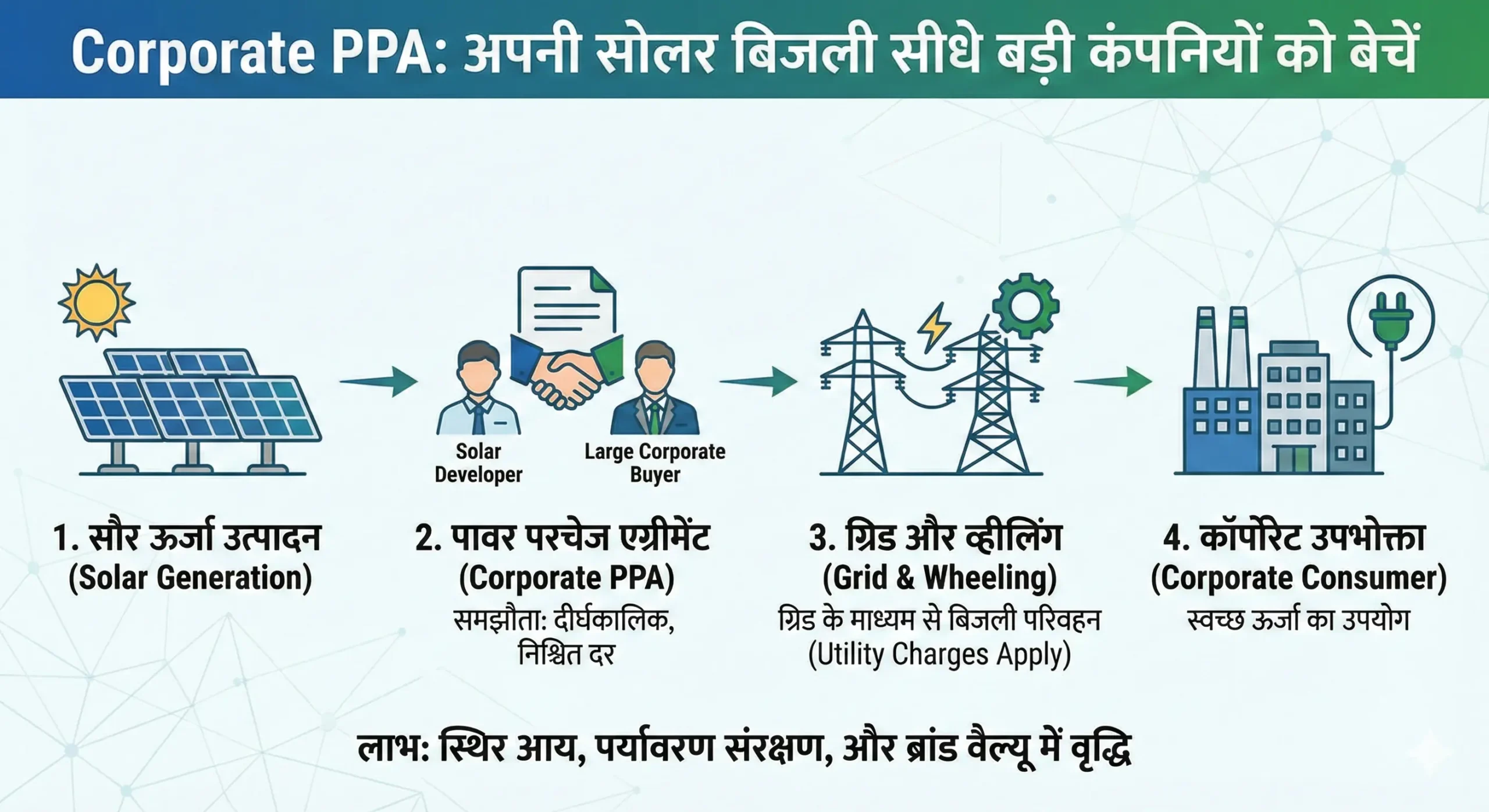
Corporate PPA: अपनी सोलर बिजली सीधे बड़ी कंपनियों को कैसे बेचें? (Full Guide 2026)
क्या आपके पास खाली जमीन है और आप सोलर प्लांट लगाकर बिजली बेचना चाहते हैं? लेकिन सरकार (DISCOM) को बिजली बेचने के बजाय, अगर आप सीधे बड़ी प्राइवेट कंपनियों (MNCs) को बिजली बेचें, तो आपको दोगुना मुनाफा हो सकता है।
इस बिज़नेस मॉडल को "Corporate PPA" या "Open Access Solar" कहते हैं। आज के समय में Tata, Adani से लेकर Google और Amazon तक, सभी कंपनियां सस्ती और ग्रीन बिजली खरीदना चाहती हैं। इस पोस्ट में हम जानेंगे कि आप इसका फायदा कैसे उठा सकते हैं।
विषय-सूची (Table of Contents)
1. कॉर्पोरेट PPA क्या है? (What is Corporate PPA?)
PPA का मतलब है Power Purchase Agreement। यह एक लंबी अवधि (15-25 साल) का कॉन्ट्रैक्ट होता है जो बिजली बनाने वाले (Generator) और बिजली खरीदने वाले (Off-taker/Buyer) के बीच होता है।
जब कोई सोलर डेवलपर अपनी बिजली सीधे किसी प्राइवेट कंपनी (जैसे- सीमेंट फैक्ट्री, डाटा सेंटर, या होटल) को बेचता है, तो इसे 'Corporate PPA' कहते हैं। इसमें बिजली की दरें (Tariff) पहले से तय कर ली जाती हैं, जो सरकारी रेट से कम होती हैं।
2. बिजली बेचने के तरीके (Business Models)
भारत में प्राइवेट बिजली बेचने के मुख्य रूप से दो मॉडल हैं। इनमें से 'Group Captive' सबसे ज्यादा फायदेमंद है।
| फीचर | Third Party Sale | Group Captive (सबसे बेस्ट) |
|---|---|---|
| क्या है? | सीधे किसी को भी बिजली बेचना। | खरीददार को प्रोजेक्ट में 26% शेयरधारक बनाना। |
| Cross Subsidy Surcharge | लागू होता है (महंगा पड़ता है)। | शून्य (माफ़ होता है)। |
| मुनाफा (Profit) | कम | बहुत ज्यादा |
3. कंपनियां आपसे बिजली क्यों खरीदेंगी? (Why Companies Buy?)
बड़ी कंपनियां सरकारी ग्रिड को छोड़कर आपसे बिजली क्यों लेंगी? इसके 3 मुख्य कारण हैं:
- भारी बचत (Cost Saving): कमर्शियल बिजली का सरकारी रेट ₹10-12 प्रति यूनिट होता है। आप उन्हें ₹5-7 में बिजली दे सकते हैं। यानी कंपनी की करोड़ों की बचत।
- Price Certainty: सरकारी बिजली के दाम हर साल बढ़ते हैं। PPA में आप 25 साल के लिए रेट फिक्स कर सकते हैं।
- ESG Goals (ग्रीन इमेज): हर बड़ी कंपनी अब "Net Zero" बनना चाहती है। आपकी सोलर बिजली उन्हें कार्बन फुटप्रिंट कम करने में मदद करती है।
4. प्रोजेक्ट शुरू करने की प्रक्रिया (Step-by-Step Process)
यह कोई छोटा काम नहीं है, इसमें समय और निवेश दोनों लगते हैं।
- Step 1: जमीन (Land): सबसे पहले ऐसी जमीन ढूंढें जहाँ सूरज की रोशनी अच्छी हो और पास में सब-स्टेशन हो।
- Step 2: ग्राहक (Off-taker): ऐसी कंपनी ढूंढें जिसकी क्रेडिट रेटिंग (Credit Rating) अच्छी हो (AA+ या AAA)। क्योंकि अगर कंपनी ने बिल नहीं भरा, तो आप फंस सकते हैं।
- Step 3: परमिशन (Open Access): राज्य के नोडल एजेंसी (State Nodal Agency) से 'ओपन एक्सेस' की मंजूरी लें।
- Step 4: PPA साइन करना: वकीलों की मदद से एक मजबूत एग्रीमेंट तैयार करें जिसमें पेमेंट की शर्तें साफ़ हों।
- Step 5: निर्माण और सप्लाई: प्लांट लगाएं और ग्रिड के माध्यम से बिजली भेजना शुरू करें।
5. ओपन एक्सेस चार्जेज (Open Access Charges)
जब आप सरकारी तारों (Grid) का इस्तेमाल करके अपनी बिजली किसी और को भेजते हैं, तो आपको कुछ टैक्स देने पड़ते हैं। इन्हें Open Access Charges कहते हैं:
- Wheeling Charge: डिस्ट्रिब्यूशन नेटवर्क इस्तेमाल करने का किराया।
- Transmission Charge: हाई-वोल्टेज लाइनों का किराया।
- Cross Subsidy Surcharge (CSS): (Group Captive में माफ़)।
- Banking Charges: अगर आप बिजली को ग्रिड में स्टोर करते हैं।
6. अक्सर पूछे जाने वाले प्रश्न (FAQs)
Q1. कम से कम कितना बड़ा प्लांट होना चाहिए?
ओपन एक्सेस के लिए कम से कम 1 MW (मेगावाट) का कनेक्शन होना ज़रूरी है। इससे छोटे प्रोजेक्ट के लिए यह मॉडल काम नहीं करता।
Q2. क्या मैं अपनी छत पर लगे सोलर से पड़ोसी को बिजली बेच सकता हूँ?
नहीं, इसे 'Peer-to-Peer' ट्रेडिंग कहते हैं जो अभी भारत में पूरी तरह लागू नहीं है। Corporate PPA ग्रिड के माध्यम से दूर स्थित कंपनियों के लिए है।
Q3. निवेश कितना लगता है?
1 MW सोलर प्लांट के लिए लगभग ₹4-5 करोड़ का खर्चा आता है। लेकिन इसका ROI (रिटर्न) बहुत अच्छा है।
Corporate PPA: How to Sell Solar Power Directly to Big Companies? (Full Guide 2026)
Do you have land and capital to invest in a Solar Plant? Instead of selling power to the government (DISCOM) at low rates, selling directly to private MNCs can double your profits.
This business model is called "Corporate PPA" or "Open Access Solar". Today, giants like Amazon, Google, and Tata are actively looking for green power suppliers. In this guide, we will explore how you can tap into this lucrative market.
Table of Contents
1. What is Corporate PPA?
PPA stands for Power Purchase Agreement. It is a long-term contract (15-25 years) between the power generator (You) and the power buyer (Corporate Off-taker).
When a solar developer sells electricity directly to a private entity (like a cement factory, data center, or hotel) via the grid, avoiding the DISCOM, it is termed a 'Corporate PPA'. The tariff is pre-decided and is mutually beneficial.
2. Business Models (How to Sell?)
There are two primary models for Open Access in India. 'Group Captive' is the industry favorite.
| Feature | Third Party Sale | Group Captive (Best Model) |
|---|---|---|
| Concept | Selling to any third party directly. | Buyer holds 26% equity in your project. |
| Cross Subsidy Surcharge | Applicable (Expensive). | Waived Off (Zero). |
| Profitability | Low to Medium | High |
3. Why Companies Buy from You?
Why would a large corporate switch from the stable government grid to you? Here are 3 reasons:
- Massive Savings: Commercial grid tariffs are ₹10-12/unit. You can offer them power at ₹5-7/unit. This saves them crores annually.
- Price Hedging: Grid prices rise every year. A PPA locks in the price for 25 years, helping companies forecast budgets.
- ESG Goals: Companies are under pressure to become "Net Zero". Buying your green energy helps them meet their sustainability targets.
4. Step-by-Step Process to Start
This is a capital-intensive business requiring careful planning.
- Step 1: Land Acquisition: Secure land with high solar irradiation and proximity to a pooling substation.
- Step 2: Find an Off-taker: Look for a company with a strong Credit Rating (AA+ or AAA). This ensures timely payments.
- Step 3: Open Access Permission: Apply for connectivity and open access approvals from the State Nodal Agency (SNA).
- Step 4: Signing PPA: Draft a robust legal agreement covering lock-in periods, payment terms, and termination clauses.
- Step 5: Commissioning: Build the plant and start injecting power into the grid.
5. Understanding Open Access Charges
Using the government's transmission lines (Grid) is not free. You or the buyer must pay Open Access Charges:
- Wheeling & Transmission Charges: Rent for using the wires.
- Cross Subsidy Surcharge (CSS): Tax to subsidize poor consumers (Waived in Group Captive).
- Banking Charges: Fee for storing excess power in the grid for later use.
6. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the minimum capacity required?
Open Access is generally allowed for consumers with a connected load of 1 MW (Megawatt) and above.
Q2. What is the biggest risk in this business?
Credit Risk: If the buyer goes bankrupt or refuses to pay, your investment is stuck. Always check the financial health of the off-taker.
Q3. What is the investment required?
Setting up a 1 MW ground-mounted solar plant costs approximately ₹4-5 Crores. However, bank financing (70%) is available.
